RM0046 Enhanced Direct Memory Access (eDMA)
Doc ID 16912 Rev 5 411/936
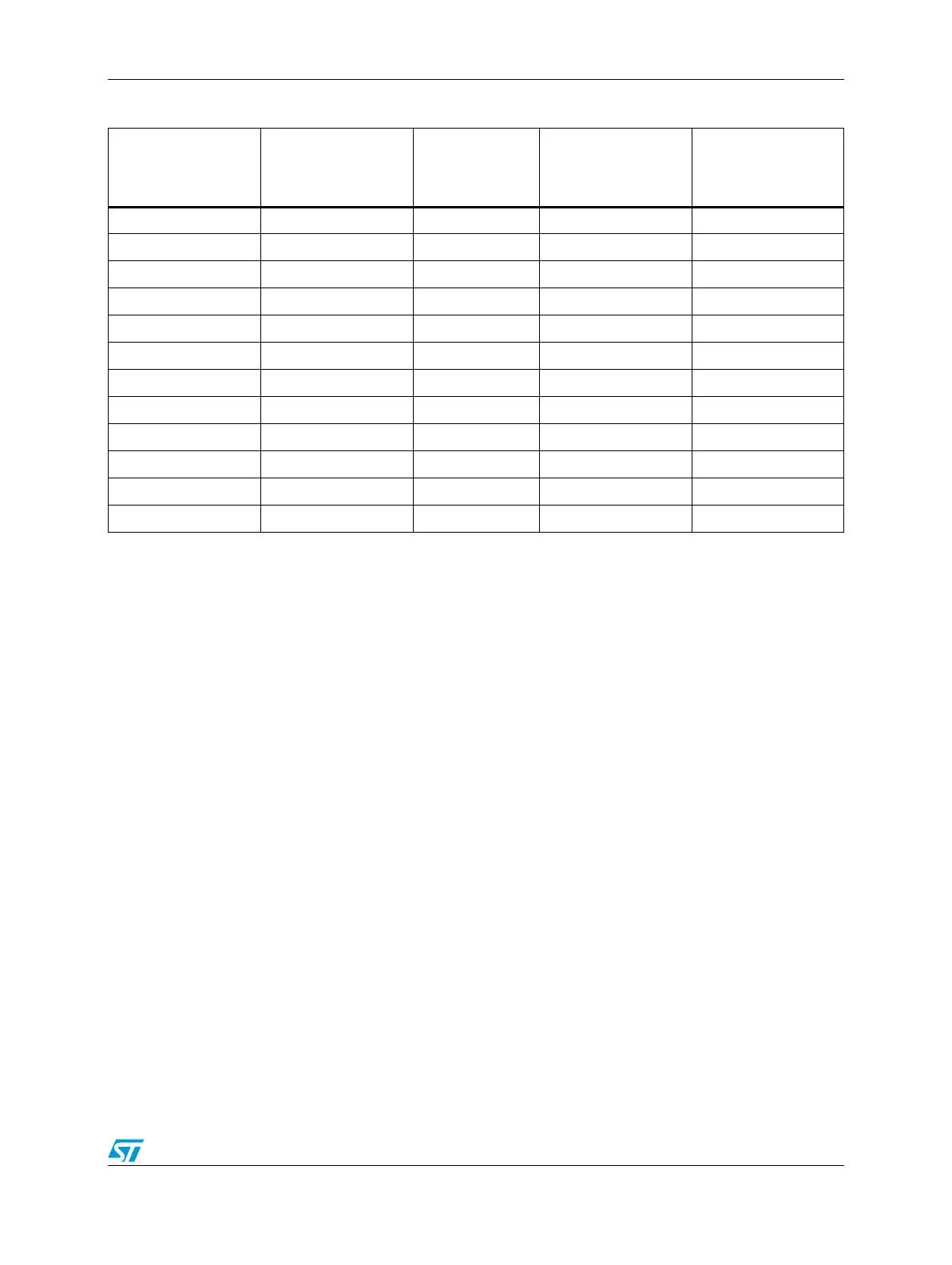
Table 194 presents a peak transfer rate comparison, measured in MBs per second where
the internal-SRAM-to-internal-SRAM transfers occur at the core’s datapath width; that is,
either 32- or 64-bits per access. For all transfers involving the slave bus, 32-bit transfer sizes
are used. In all cases, the transfer rate includes the time to read the source plus the time to
write the destination.
The second performance metric is a measure of the number of DMA requests that can be
serviced in a given amount of time. For this metric, it is assumed the peripheral request
causes the channel to move a single slave-mapped operand to/from internal SRAM. The
same timing assumptions used in the previous example apply to this calculation. In
Table 194. eDMA peak transfer rates (MB/Sec)
System Speed,
Transfer Size
Internal SRAM-to-
Internal SRAM
32-bit Slave-to-
Internal SRAM
Internal SRAM-to-
32-bit Slave
(buffering disabled)
Internal SRAM-to-
32-bit Slave
(buffering enabled)
66.7 MHz, 32-bit 66.7 66.7 53.3 88.7
66.7 MHz, 64-bit 133.3 66.7 53.3 88.7
66.7 MHz, 256-bit
(1)
213.4 N/A
(2)
N/A
2
N/A
2
83.3 MHz, 32-bit 83.3 83.3 66.7 110.8
83.3 MHz, 64-bit 166.7 83.3 66.7 110.8
83.3 MHz, 256-bit
1
266.6 N/A
2
N/A
2
N/A
2
100.0 MHz, 32-bit 100.0 100.0 80.0 133.0
100.0 MHz, 64-bit 200.0 100.0 80.0 133.0
100.0 MHz, 256-bit
1
320.0 N/A
2
N/A
2
N/A
2
132.0 MHz, 32-bit 132.0 132.0 105.6 175.6
132.0 MHz, 64-bit 264.0 132.0 105.6 175.6
132.0 MHz, 256-bit
1
422.4 N/A
2
N/A
2
N/A
2
1. A 256-bit transfer occurs as a burst of four 64-bit beats.
2. Not applicable: burst access to a slave port is not supported.
 Loading...
Loading...