RM0046 Enhanced Direct Memory Access (eDMA)
Doc ID 16912 Rev 5 413/936
A general formula to compute the peak request rate (with overlapping requests) is:
Equation 13
PEAKreq = freq / [entry + (1 + read_ws) + (1 + write_ws) + exit]
where:
PEAKreq — peak request rate
freq — system frequency
entry — channel startup (four cycles)
read_ws — wait states seen during the system bus read data phase
write_ws — wait states seen during the system bus write data phase
exit — channel shutdown (three cycles)
For example: consider a system with the following characteristics:
● Internal SRAM can be accessed with one wait-state when viewed from the system bus
data phase.
● All slave reads require two wait-states, and slave writes three wait-states, again viewed
from the system bus data phase.
● System operates at 150 MHz.
For an SRAM to slave transfer,
Equation 14
PEAKreq = 150 MHz / [4 + (1 + 1) + (1 + 3) + 3] cycles = 11.5 Mreq/sec
For an slave to SRAM transfer,
Equation 15
PEAKreq = 150 MHz / [4 + (1 + 2) + (1 + 1) + 3] cycles = 12.5 Mreq/sec
Assuming an even distribution of the two transfer types, the average peak request rate is:
Equation 16
PEAKreq = (11.5 Mreq/sec + 12.5 Mreq/sec) / 2 = 12.0 Mreq/sec
The minimum number of cycles to perform a single read/write, zero wait states on the
system bus, from a cold start (no channel is executing, eDMA is idle) are the following:
● 11 cycles for a software (TCD.START bit) request
● 12 cycles for a hardware (eDMA peripheral request signal) request
Two cycles account for the arbitration pipeline and one extra cycle on the hardware request
resulting from the internal registering of the eDMA peripheral request signals. For the peak
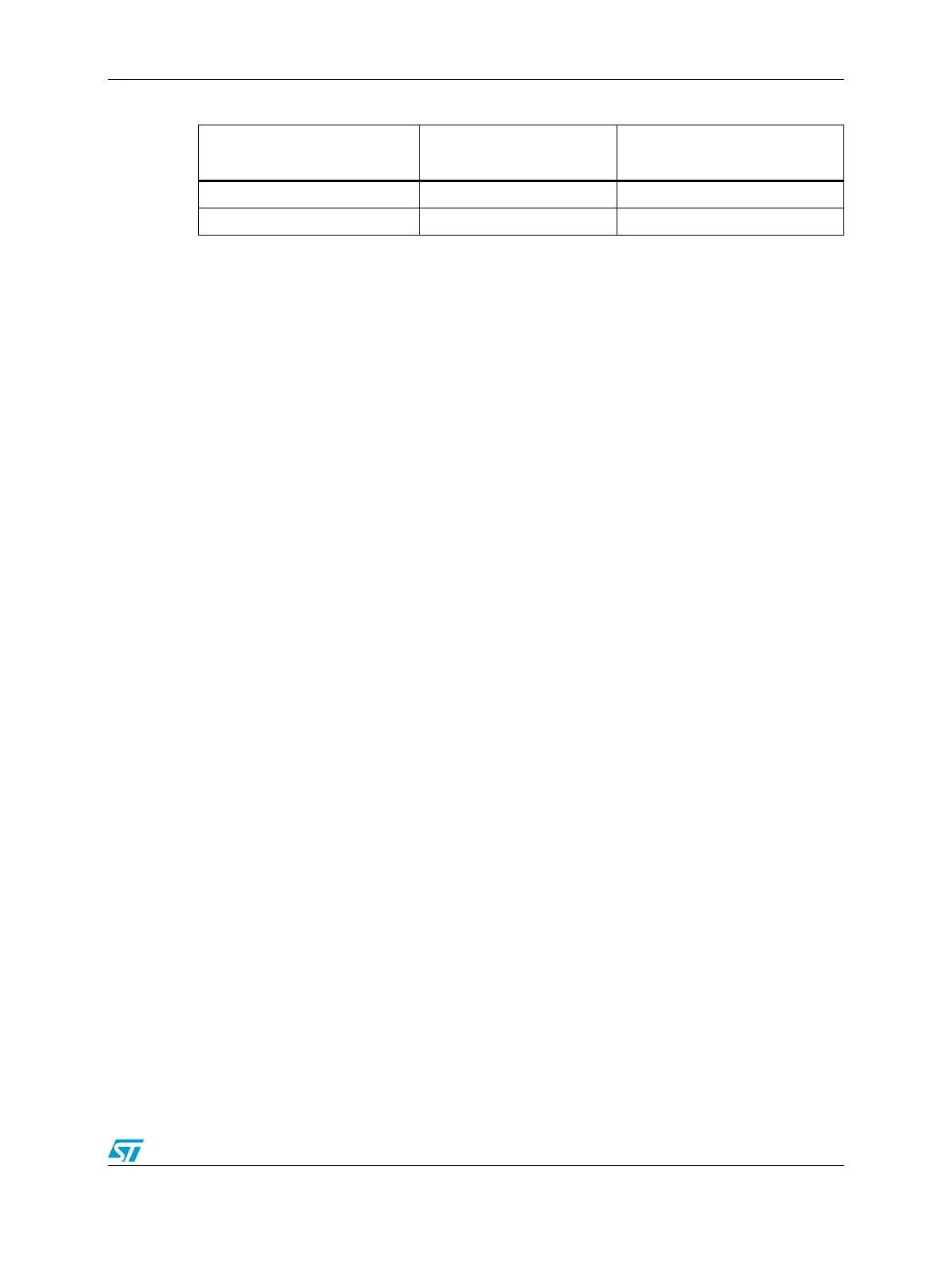
133.3 14.8 11.6
150.0 16.6 13.0
Table 195. eDMA peak request Rate (MReq/sec) (continued)
System Frequency
(MHz)
Request Rate
(Zero Wait States)
Request Rate
(with Wait States)
 Loading...
Loading...