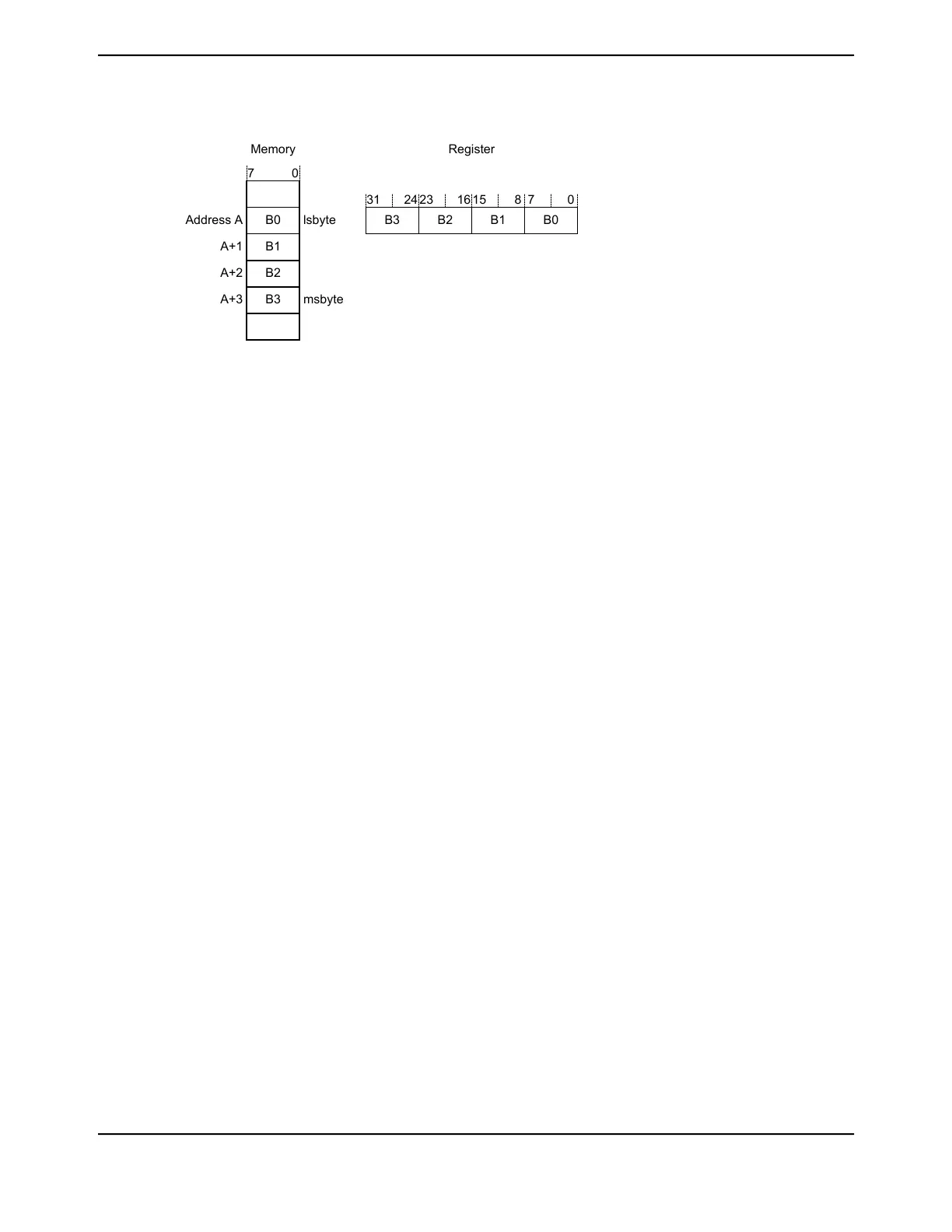
Figure 2-5. Data Storage
Memory Register
Address A
A+1
lsbyte
msbyte
A+2
A+3
07
B0B1B3 B2
31 2423 1615 8 7 0
B0
B1
B2
B3
2.4.7 Synchronization Primitives
The Cortex-M4F instruction set includes pairs of synchronization primitives which provide a
non-blocking mechanism that a thread or process can use to obtain exclusive access to a memory
location. Software can use these primitives to perform a guaranteed read-modify-write memory
update sequence or for a semaphore mechanism.
Note: The available pairs of synchronization primitives are only available for single processor use
and should not be used with multi-processor systems.
A pair of synchronization primitives consists of:
■ A Load-Exclusive instruction, which is used to read the value of a memory location and requests
exclusive access to that location.
■ A Store-Exclusive instruction, which is used to attempt to write to the same memory location and
returns a status bit to a register. If this status bit is clear, it indicates that the thread or process
gained exclusive access to the memory and the write succeeds; if this status bit is set, it indicates
that the thread or process did not gain exclusive access to the memory and no write was
performed.
The pairs of Load-Exclusive and Store-Exclusive instructions are:
■ The word instructions LDREX and STREX
■ The halfword instructions LDREXH and STREXH
■ The byte instructions LDREXB and STREXB
Software must use a Load-Exclusive instruction with the corresponding Store-Exclusive instruction.
To perform an exclusive read-modify-write of a memory location, software must:
1. Use a Load-Exclusive instruction to read the value of the location.
2. Modify the value, as required.
3. Use a Store-Exclusive instruction to attempt to write the new value back to the memory location.
4. Test the returned status bit.
June 18, 2014112
Texas Instruments-Production Data
The Cortex-M4F Processor

 Loading...
Loading...











