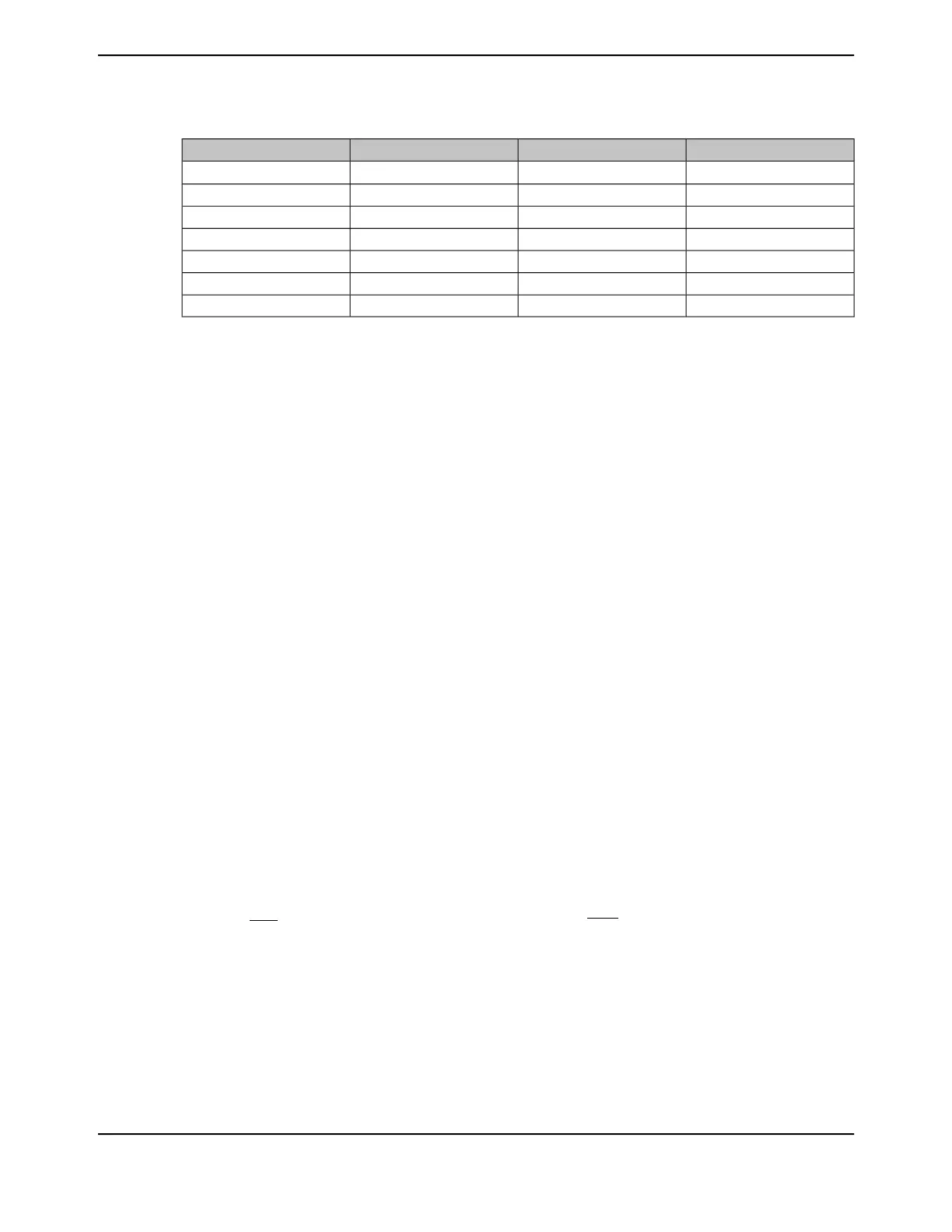
Table 5-2. Reset Sources (continued)
On-Chip Peripherals Reset?JTAG Reset?Core Reset?Reset Source
Yes
a
Pin Configuration OnlyNoSoftware Peripheral Reset
YesPin Configuration OnlyYesWatchdog Power-On Reset
YesPin Configuration OnlyYesWatchdog System Reset
YesPin Configuration OnlyYesHIB Module Power-On Reset
YesPin Configuration OnlyYesHIB Module System Reset
YesPin Configuration OnlyYesHSSR Reset
YesPin Configuration OnlyYesMOSC Failure Reset
a. Programmable on a module-by-module basis by using the individual peripheral Software Reset Registers starting at
System Control offset 0x500
After a reset, the Reset Cause (RESC) register is set with the reset cause. The bits in this register
are sticky and maintain their state across multiple reset sequences. A bit in the RESC register can
be cleared by writing a 0.
5.2.2.2 Boot Configuration
After Power-On-Reset (POR) and device initialization occurs, the hardware loads the stack pointer
from either flash or ROM based on the presence of an application in flash and the state of the EN
bit in the BOOTCFG register. If the flash address 0x0000.0004 contains an erased word (value
0xFFFF.FFFF) or the EN bit is of the BOOTCFG register is clear, the stack pointer and reset vector
pointer are loaded from ROM at address 0x0100.0000 and 0x0100.0004, respectively. The boot
loader executes and configures the available boot slave interfaces and waits for an external memory
to load its software.
If the check of the Flash at address 0x0000.0004 contains a valid reset vector value and the
BOOTCFG register does not indicate the boot loader, the boot sequence causes the stack
pointer/reset vector fetch from Flash. This application stack pointer and reset vector is loaded and
the processor executes the application directly.
Note: If the device fails the initialization phase, it toggles the TDO output pin as an indication the
device is not executing. This feature is provided for debug purposes.
5.2.2.3 Externally Generated Power-On Reset (POR)
Note: The JTAG controller can be reset by a power-on reset or by holding the TMS pin to high
for 5 clock cycles.
During an externally generated POR, the internal Power-On Reset (POR) circuit monitors the power
supply voltage (V
DD
) and generates a reset signal to all of the internal logic including JTAG when
the power supply ramp reaches a threshold value (V
POR
). Reset does not complete if specific voltage
parameters are not met as defined in the Electrical Characteristics chapter. For applications that
require the use of an external reset signal to hold the microcontroller in reset longer than the internal
POR, the RST input may be used as discussed in “External RST Pin” on page 223. Holding this pin
active can keep the initialization process from starting even though power-on reset has occurred.
This is useful in in-circuit testing and other situations where it is desirable to delay the operation of
the device until an external supervisor has released.
The Power-On Reset sequence is as follows:
1. The microcontroller waits for internal POR to go inactive.
June 18, 2014222
Texas Instruments-Production Data
System Control

 Loading...
Loading...











