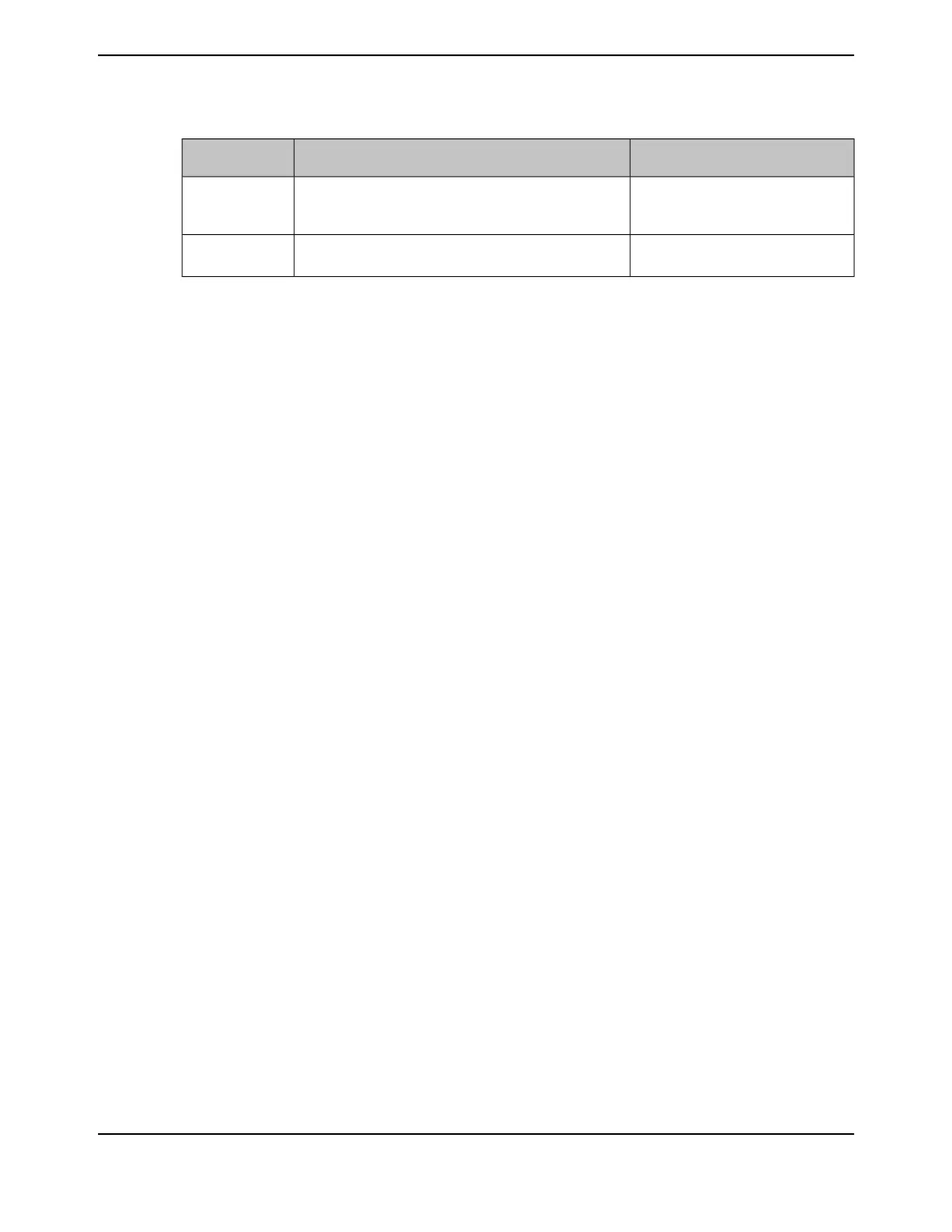
Table 12-2. Endian Configuration with Bit Reversal (continued)
Configuration with Bit Reversal (BR =
1)
Initial Endian ConfigurationENDIAN Encoding
B1[8:15],B0[0:7],B3[24:31],B2[16:23]Half-words are swapped but bytes are not swapped in
half-word.
{B1[15:8], B0[7:0], B3[31:24], B2[23:16]}
0x2
B0[0:7],B1[8:15],B2[16:23],B3[24:31]Bytes are swapped in half-words and half-words are swapped
{B0[7:0], B1[15:8], B2[23:16], B3[31:24]}
0x3
12.2 Initialization and Configuration
The following describes the initialization and configuration procedures of the CRC module.
12.2.1 CRC Initialization and Configuration
The CRC engine works in push through mode, which means it works on streaming data. This section
describes the steps for initializing the CRC module:
1. Enable the CRC by setting the R0 bit in the CRC Module (RCGCCM) register, System Control
offset 0x674.
2. Configure the desired CRC data size, bit order, endian configuration and CRC type by
programming the CRC Control (CRCCTRL) register, offset 0x400.
3. If the CRC value has not been initialized to all 0s or all 1s using the INIT field in the CRCCTRL
register, program the initial value in the CRC SEED/Context (CRCSEED) register, offset 0x410.
4. Repeatedly write the DATAIN field in the CRC Data Input (CRCDIN) register, offset 0x414. If
the SIZE bit in the CRCCTRL register is set to select byte, the CRC engine operates in byte
mode and only the least significant byte is used for CRC calculation.
5. When CRC is finished, read the CRCSEED register for the final result. If using post-processing,
the raw CRC result is stored in the CRCSEED register and the final, post-processed result can
be read from the CRC Post-Processing Result (CRCRSLTPP) register, offset 0x418.
Post-processing options are selectable through the OBR and OLNV bits of the CRCCTRL register.
Alternatively a software µDMA channel can be configured to copy data from the source into the
CRCDIN register. When configuring the µDMA, the destination should be configured to not increment.
For more information on how to configure the µDMA, refer to “Micro Direct Memory Access
(μDMA)” on page 678.
12.2.1.1 Data Endian Convention for the CRC Engine
If the input stream is expressed as a byte stream, Din, where Din = {D0, D1, D2, D3, D4, D5, D6,
D7, D8, D9, D11, D12, D13, D14, D15, D16.....}, then data should be fed to the CRC engine as
follows:
■ If operating in Byte mode, the CRCDIN register should be written in the following order:
1. {00, 00, 00, D0}
2. {00, 00, 00, D1}
3. {00, 00, 00, D2}
June 18, 2014948
Texas Instruments-Production Data
Cyclical Redundancy Check (CRC)

 Loading...
Loading...











