Data Transfer
3-88 ADSP-214xx SHARC Processor Hardware Reference
Bursts are not divisible. During reads, all DDR2 data are received
and on-chip masked by the DDR2 controller. For single write
access in SISD mode, the 3rd and 4th data needs to be masked.
The data masking (DDR2_DM1-0 signal) is only performed during
write operations as shown in Table 3-18.
SIMD write access to the DDR2 memory should be even address
aligned. If odd address aligned, the throughput is reduced by a fac-
tor of 2. This does not apply to SIMD reads or any SISD mode.
For more information on SIMD access, see the SHARC Processor
Programming Reference.
External Instruction Fetch
The processors support direct fetch of instructions from external memory,
using the 16-bit external port. Fetching is supported from external mem-
ory bank 0 space which is selected by
MS0. This external memory can
either be SDRAM, or asynchronous memory, such as SRAM or flash.
While 16-bit to 48-bit packing is supported when the external
memory is SDRAM, the external asynchronous memory interface
(AMI) also supports 8/16-bit to 48-bit instruction packing.
Interrupt Vector Table (IVT)
The interrupt vector table can be located in the internal ROM (0x80 000,
IIVT bit = 0) or internal RAM (0x8C 000, IIVT bit = 1) based on the
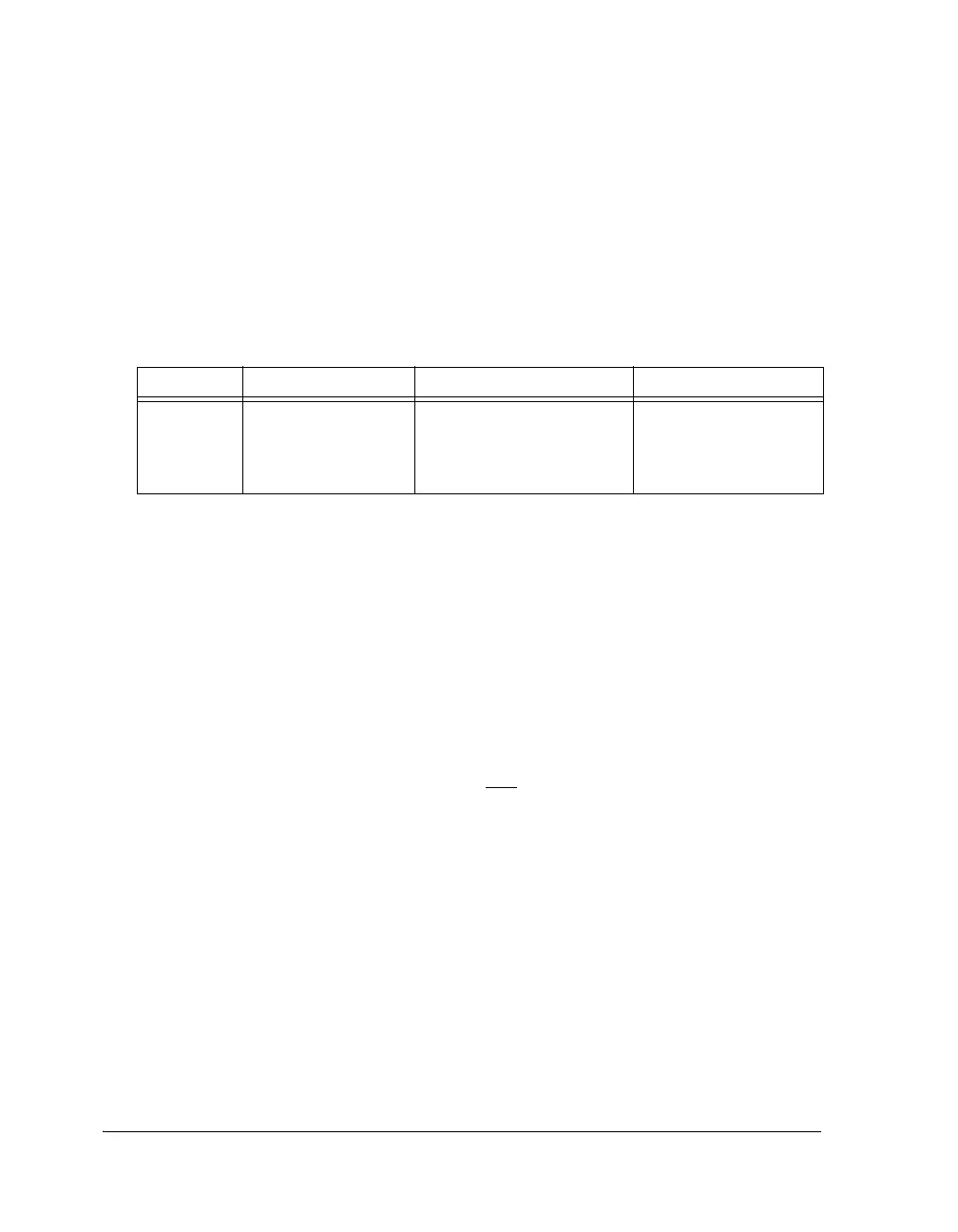
Table 3-18. DDR2 SISD Access
Access Logical x32 Physical x16 Comment
Explicit only DM(0x200000) = R0; DM(0x400000) = R0;(LSW)
DM(0x400001) = R0;(MSW)
DM(0x400002) = S0;(LSW)
DM(0x400003) = S0;(MSW)
DDR2_DM1–0 = low
DDR2_DM1–0 = low
DDR2_DM1–0 = high
DDR2_DM1–0 = high

 Loading...
Loading...