Interrupts
5-4 ADSP-214xx SHARC Processor Hardware Reference
DMA Transfer
Two DMA channels are used for memory-to-memory DMA transfers. The
write DMA channel has higher priority over the read channel. The trans-
fer is started by a write DMA to fill up the MTM buffer with a 2 x 32-bit
word. Next, the buffer is read back over the same IOD bus to the new des-
tination. With a two position deep buffer and alternate write and read
access over the same bus, throughput is limited. The memory-to-memory
DMA control register (MTMCTL) allows programs to transfer blocks of
64-bit data from one internal memory location to another. This register
also allows verification of current DMA status during writes and reads.
Interrupts
There are two DMA channels; one write channel and one read channel.
When the transmission of a complete data block is performed, each chan-
nel will generate an interrupt to signal that the entire block of data has
been processed. Note that the write and read interrupts (P15I, if the MTMI
bit in the IMASK register is enabled) are very close to each other, so only
one interrupt is triggered.
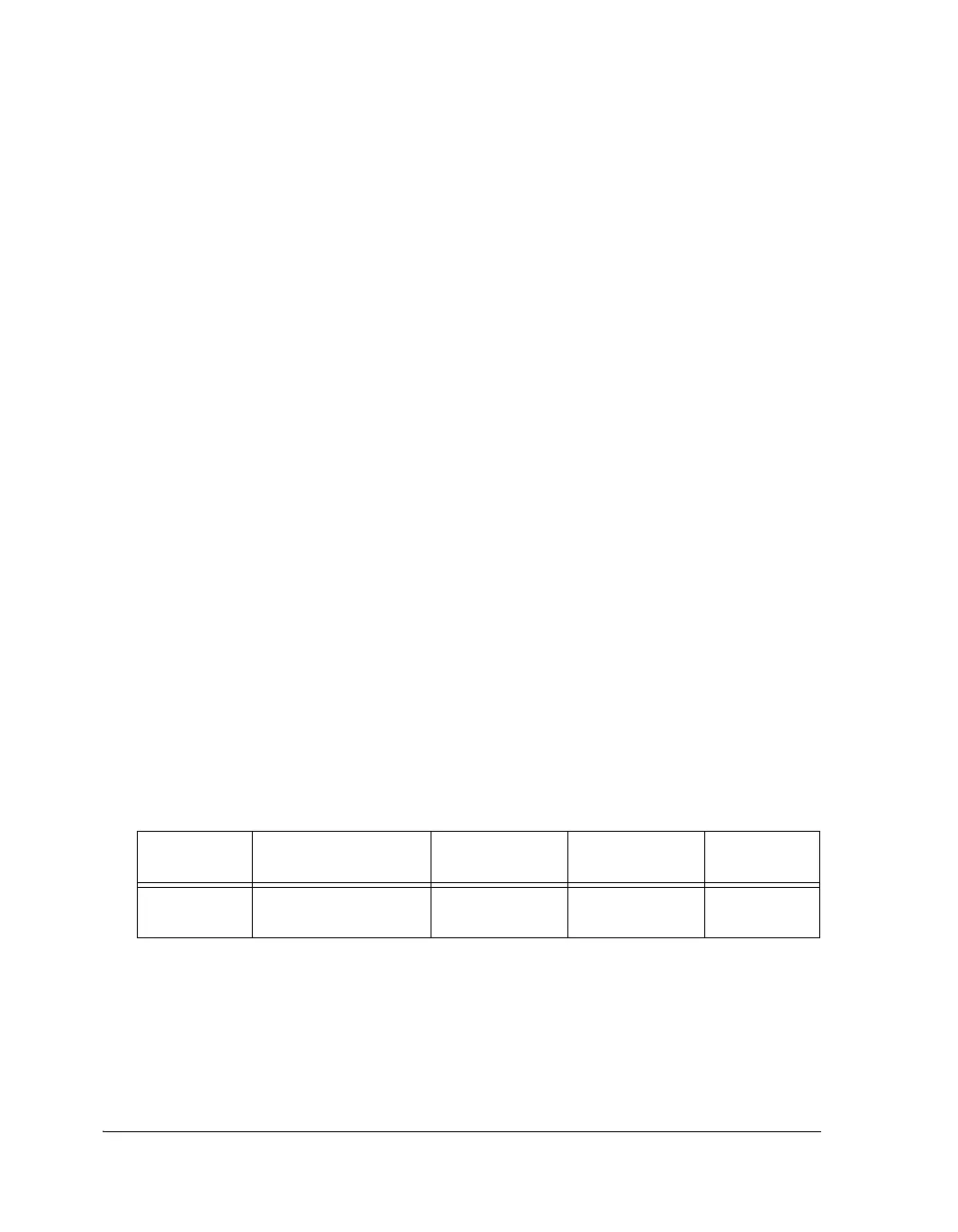
Table 5-2 provides an overview of MTM interrupts.
Table 5-2. MTM Interrupt Overview
Interrupt
Source
Interrupt Condition Interrupt
Completion
Interrupt
Acknowledge
Default IVT
MTM
(2 channels)
– WR DMA done
– RD DMA done
Internal transfer
completion
RTI instruction P15I

 Loading...
Loading...