LF1 RF1 LF2 RF2
CLK
FS
AXR4
LS1 RS1 LS2 RS2AXR5
C1 LFE1AXR6 C2 LFE2
AXEVTO
AREVTO
AXEVTE
AREVTE
AXEVTO
AREVTO
AXEVTE
AREVTE
AXEVTO
AREVTO
LF3
LS3
C3
Transmit
Receive
0 1 0 1 0
www.ti.com
Functional Description
Here are some guidelines on using the different DMA events:
• Either use AXEVT, or the combination of AXEVTO and AXEVTE, to service the McASP. Never use all
three at the same time. Similarly for receive, either use AREVT, or the combination of AREVTO and
AREVTE.
• The McASP generates transmit DMA events independently from receive DMA events; therefore,
separate schemes can be used for transmit and receive DMA. For example, scenario 1 could be used
for the transmit data (AXEVT) and scenario 2 could be used for the receive data (AREVTO, AREVTE),
and conversely.
Note the difference between DMA event generation and the CPU interrupt generation. DMA events are
generated automatically upon data ready; whereas CPU interrupt generation needs to be enabled in the
XINTCTL/RINTCTL register.
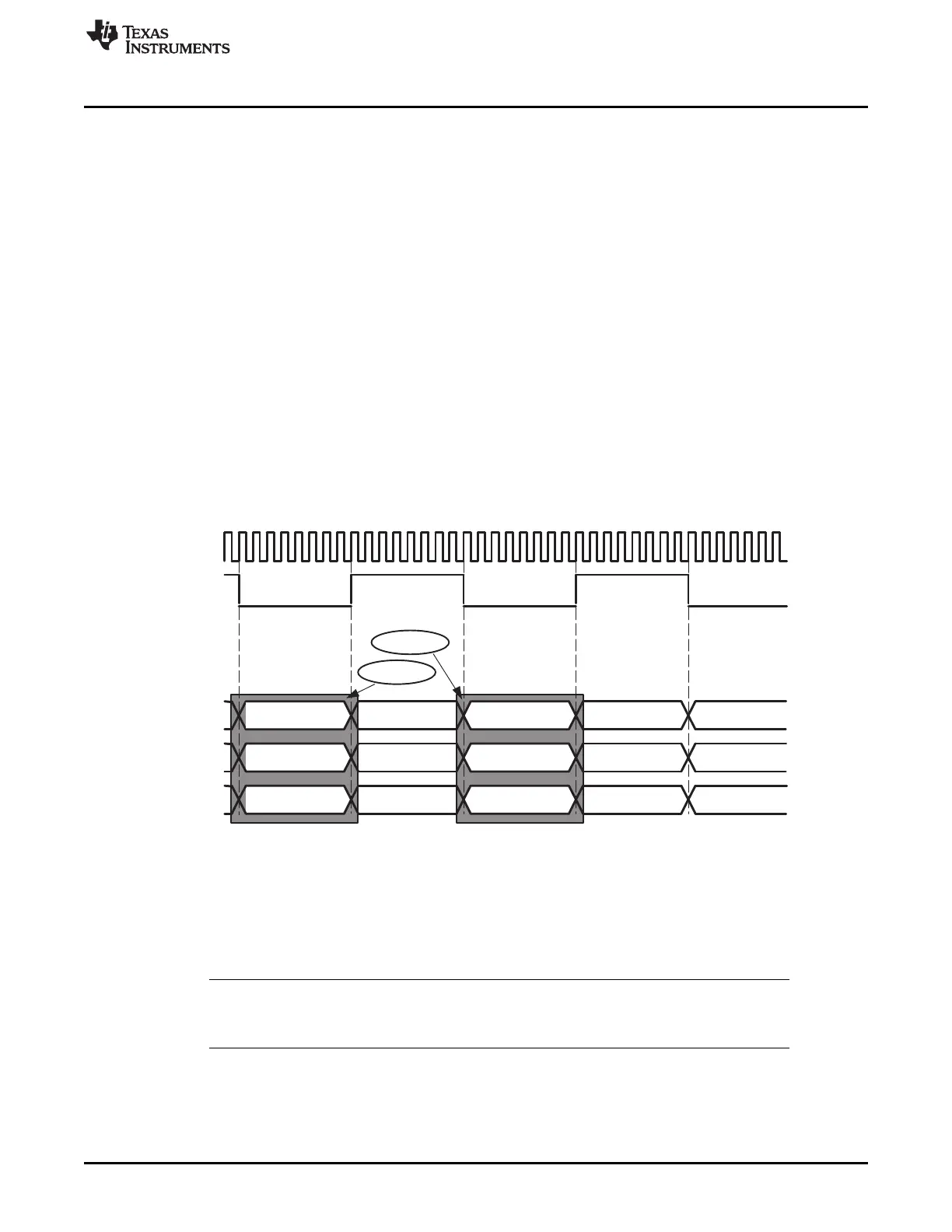
In Figure 22-37, scenario 2, each transmit DMA request is for data in the next time slot, while each receive
DMA request is for data in the previous time slot. For example, Figure 22-38 shows a circled AXEVTE
event for an even time slot transmit DMA request. The transmitter always requests a DMA transfer for
data it will need to transmit during the next time slot. So, in this example, the circled event AXEVTE is a
request for data for samples LF2, LS2, and C2.
On the other hand, the circled AREVTE event is an even time slot receive DMA request. The receiver
always requests a DMA transfer for data it received during the previous time slot. In this example, the
circled event AREVTE is a request for samples LF1, LS1, and C1.
Figure 22-38. DMA Events in an Audio Example
22.3.15 Power Management
The McASP can be placed in reduced power modes to conserve power during periods of low activity.
22.3.16 Emulation Considerations
NOTE: The receive buffer registers (RBUFn) and transmit buffer registers (XBUFn) should not be
accessed by the emulator when the McASP is running. Such an access will cause the
RRDY/XRDY bit in the serializer control register n (SRCTLn) to be updated.
The McASP does not support the emulation suspend.
3825
SPRUH73H–October 2011–Revised April 2013 Multichannel Audio Serial Port (McASP)
Submit Documentation Feedback
Copyright © 2011–2013, Texas Instruments Incorporated

 Loading...
Loading...











